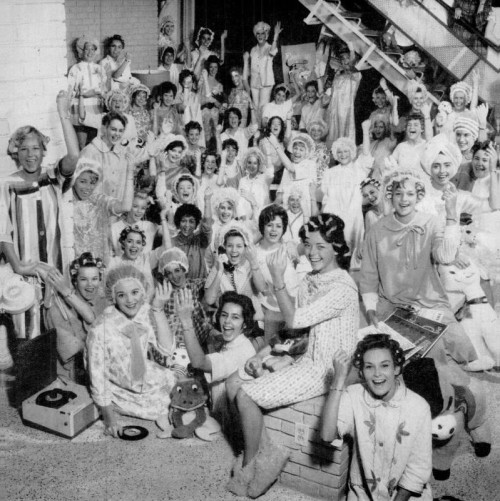
According to this ad for Bulova watches, it’s time for a pajama party. Circa 1963; via Simple Dreams.
Category: Don We Now Our Gay Apparel
Fashion facts and fabulously kitschy clothing.
Yes We Can! Rosie The Riveter Fashions
Proof that this look was in fashion for women before there was an American home front and a The War Advertising Council’s Women in War Jobs campaign with Rosie the Riveter.
Scanned from New Fashions For You & Your Home, Spring Summer 1940, published by Singer Sewing Machine Company (I’ve listed it at eBay), this page features patterns by Du Barry.
More scans from this vintage publication at my Tumblr.
Kaptain Kool & The Kongs On Gender & Fashion
From issue number two of The New Krofft Supershow comic (1978), deep insights into gender and fashion…
In panel two:
Turkey, why are you wearing your socks wrong side out?
Shh, there’s a hole on the other side!
‘Cuz men are stupid; they never change or replenish their socks — or underwear.
(Confession: I sit here right now, my bare toe sticking out of — wait for it! — my husband’s sock. Why? I am in need of purchasing more socks for myself. …However, it is so fun to say, “My toe is sticking out of hubby’s sock.” That’s how close we are!)
In panel three:
Oh, these pants are tighter than my skin!
How can anything be tighter than your skin?
Easy! She can sit down in her skin, but she sure can’t sit down in those pants.
‘Cuz women are stupid; they kill themselves for fashion.
(Confession: I wore tight Jordache jeans. They were tight… But obviously if I wore them to school or took a ride in a car, I could sit in them. …And I do recall that men’s jeans were just as tight. In fact, I vaguely recall it being some sort of a competition.)
PS Bonus points for the ironic “Watch Your Step” sign in the background of that last panel.
Shoes Like A Chastity Belt

With the current state of affairs — i.e. republicans trying to defund Planned Parenthood, it seems these Knee High Converse shoes might become affordable birth control. (Yes, even at $60+ they are a one-time purchase.) Since, even with the zipper, it takes a good 15-20 minutes to get them on or off (my 14 year old timed herself and tells me so), greatly delaying the removal of the unfortunately popular skinny jeans, jeggings, etc. (which are so tight they must be completely removed), these shoes might just be as good as a chastity belt.
Image via.
PS These shoes come in more than just black; in case you’d like your birth control to match more of your wardrobe.
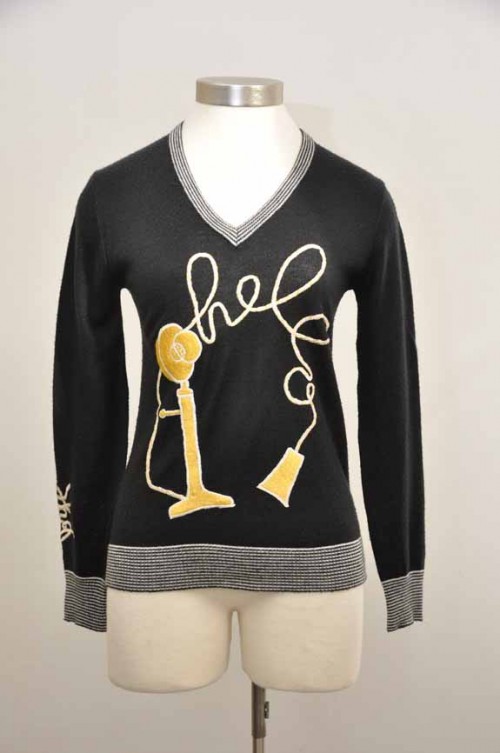
Because Men Are Already Talking To Your Chest
How about this vintage novelty telephone sweater from the 50’s? Via terrasita.
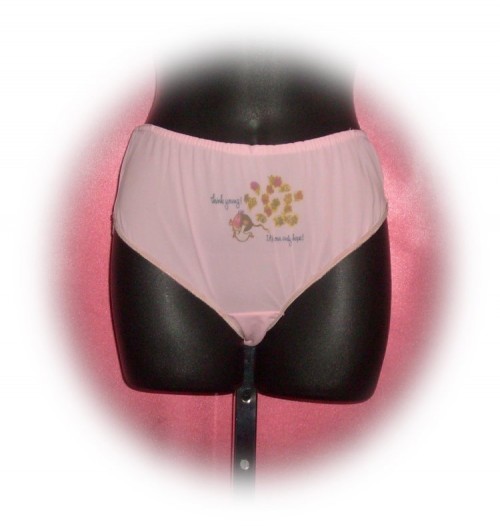
Those 70s Pedophile Panties
Completely inappropriate panties with “Think Young! It’s Our Only Hope!” printed on them — with a little girl in her nightdress running screaming into the night. Oh, ish. Via pink girl vintage.
While American Was being Born… Ladies Who Didn’t Have Enough Sense To Come In Out Of The Rain
From a Modern Woman magazine from the 40’s, some interesting news…
For the benefit of eighteenth century ladies who didn’t have enough sense to come in out of the rain, a Parasol Lend-company flourished in Paris, France, about the year 1776. Negro attendants carried the parasols and collected payment upon delivering a charge at her destination. In those times, a parasol cost too much for an average woman to own.
Nonsensical Marketing Magic
I think Betsey Johnson must hire non-English speaking peoples to name her products, using some translation software to easily convert their ideas to nonsensical gibberish now… Because Locking Lips Hobo sounds like a lot of the spam I receive.
Who knows, maybe such random word alignment actually sells stuff>
I found this gem in my Shop It To Me Sale Mail Alert.
It’s Like A Pucci In The Face
 If you have difficulty being a woman and knowing what you want, you can blame it on Emilio Pucci‘s death.
If you have difficulty being a woman and knowing what you want, you can blame it on Emilio Pucci‘s death.
In this vintage lingerie ad for Pucci‘s Fiore Festa line for Formfit Rogers the text boasts, “How does he know what women want before they know themselves?”
Because women are such fickle stupid creatures, we don’t even know what we want to wear.
Even if all we do is shop.
Right?
It’s true; I have conflicting responses to vintage lingerie advertising. But who doesn’t?
(And if you don’t, then we should talk!)
Image via devocanada.
Because There’s Nothing More Shameful For A Boy Than Looking Like A Girl
One of the “367 prize winning household hints” Hint Hunt booklet (the better ones will be found at my vintage home ec site, Things Your Grandmother Knew), this tip “for mothers only” advises that “to cure boys of the habit of not keeping shirttails tucked in, sew an edging of lace around the bottom of the lad’s shirt.”
Weasel Pouches – I’m Just Sayin’…
 Chain Mesh Cigarette Cases are now on sale for just $4.99 — which reminds me…
Chain Mesh Cigarette Cases are now on sale for just $4.99 — which reminds me…
My aunt, and pretty much everyone else on my mom’s side of the family, had a cigarette case which doubled as a coin purse; it was called a “weasel pouch.”
Sale found via Shop It To Me sale mail.
Of Goldie Hawn & Babydoll Dresses
When I saw this 1960’s mod-meets-Edwardian little black velvet mini dress, which looks like a jumper over cream ruffled blouse and trimmed in gold braiding, I instantly thought of Goldie Hawn.
Goldie, like the Atria dress above, had an incredible way of taking a simple, even older looking fashion design, and breathing new life into it.
Some people think of Goldie Hawn — and any babydoll mini dress, really — as an exploitative thing. They tend to view short feminine dresses as something sinister involving the sexualization of children. But I don’t think that’s quite right… At least not always.
If you remove the ‘babydoll’ from the description, and just look at the dresses, they do express traits we tend to equate with children: simplicity, innocence, delight in bright cheery colors (not dwelling in those dull colors symbolical of adult conformity), the unencumbered freedom of a swinging skirt above bare mobile legs. But are these things only for children?
Sure, I think Goldie’s warm, sunny, playful confidence was sexy — but not one that risked the promotion of pedophilia. You ought not mistake childlike for being an actual child.
Like so many of the characters Goldie played, she may have seemed direct and simple to the point of silliness, but her innocence was anything but dumb; possessing the wisdom of a child and the charm of childlike innocence without being a child is beautiful. And Goldie matched that beauty with her own natural beauty which didn’t rely on lots of accessories and artifice. For a woman to be so comfortable in her own skin, happy to express that she was a girl — not just unapologetically female, but celebrating femininity — that’s spectacular.
In the 60’s and 70’s, Goldie was a visual reminder to avoid, as The Graduate would say, the ‘plastics,’ the mold-fitting uniformity of the establishment. But unlike the cold mod of Twiggy which held you at a disdainful fashion distance (and at a fashionable distance of social disdain), Goldie invited you in to play with her. Not (simply) sexually; but to come play, laugh, learn, and experience with her.
In truth, such babydoll dresses better suit the slim and less ‘womanly’ shaped among us. In part because curves require garments with more structure to restrain &/or retain than most babydoll dresses have. But primarily the problem isn’t so much that babydoll dresses are less apt at covering ample bosoms and rounder aft-areas (things which could be addressed if fashion was properly sized for real women’s bodies), but rather that society deems such displays of female form, however natural, as solicitations — offers to men that women and children have no right to refuse.
That people don’t always see the more honest virtues in those retro babydoll dresses makes me more than a little sad; it makes me ill.
In Case It’s Raining Men…
Hallelujah, Weather Girls, here’s a red retro bolero with umbrellas!
Glove Boxing: Taking Off The Gloves Regarding Gloves
The popularity of gloves is said to have begun in the 16th century when Catherine de Médicis, queen consort of Henry II of France, jealous of well-dressed men whose wardrobes included gloves, began a campaign to make them part of ladies’ fashion. Catherine’s powers were noted in many areas, including fashion; not only did she succeed in making gloves popular, but after it was discovered that both she and the recently deceased Jeanne d’Albret shared the same glove supplier and perfumier, it was rumored that Catherine had killed Jeanne via poisoned gloves (an autopsy revealed otherwise, but it says something of Catherine — and the popularity of gloves; this story is included in Alexandre Dumas’s 1845 novel of the French Renaissance, La Reine Margot).
By the mid-nineteenth century gloves were de rigueur, making it more than unseemly for a woman to leave the house without wearing gloves — but out-right indecent. Heck, a proper lady wouldn’t be seen barehanded even indoors.
Antique Personal Possessions quotes this letter to The Queen from 1862:
In every costume but the most extreme neglige a lady cannot be said to be dressed except she is nicely and completely gloved; and this applies equally to morning, afternoon, dinner, and evening dress.
Of course it was also unladylike to wear soiled gloves. Glove cleaners were sometimes used (by cheating cheapskates), but as kidskin (and doeskin) gloves were preferred, most cleaning products failed to clean or effectively hide marks on leather. So gloves were purchased by the dozens and stored in the essential glove box.
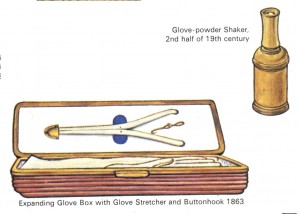 Along with gloves themselves and a scented sachet to perfume the gloves, glove boxes held materials essential for putting gloves on: glove stretcher, glove button-hook, and glove-powder shaker.
Along with gloves themselves and a scented sachet to perfume the gloves, glove boxes held materials essential for putting gloves on: glove stretcher, glove button-hook, and glove-powder shaker.
These glove-powderers contained glove powders which not only were to aid in the easing on of tight gloves, but which were often sold as softening and bleaching the hands. Can you imagine what ingredients these powders had? Lead was an incredibly common ingredient in powders and cosmetics of all sorts — how rapidly such chemicals would adhere to and be absorbed by warm moist hands. Obviously Catherine de Médicis needn’t have added anything unusual to Jeanne d’Albret’s gloves if she wanted her dead; but by the same token, Catherine was slowly killing herself as well.
The wearing of gloves, of course, was yet another social rule which distinguished between the working class and the wealthy. Wearing pretty light-colored gloves kept pretty light-colored hands easily discernible from tanned working hands; making the wearing of gloves vital for those with (or seeking) social standing.
The wealthy not only could afford the gloves but the leisure time to wear them — even if wearing gloves kept their hands nearly as useless as if kept in handcuffs.
Certainly this glove-wearing business was far more debilitating than corsets. Which is why I’ve always rather viewed antique glove boxes as little coffins.
Corsets Bound To Stay Suffrage
 If you’ve been following along with my corset history workshop, you’ve read about the debunking of the science behind death-by-corset claims and seen some of the evidence why science and medicine was manipulated due to social hysteria; but what we are now left wondering is just how early feminists were swayed into backing the anti-corset science.
If you’ve been following along with my corset history workshop, you’ve read about the debunking of the science behind death-by-corset claims and seen some of the evidence why science and medicine was manipulated due to social hysteria; but what we are now left wondering is just how early feminists were swayed into backing the anti-corset science.
The answer, as always, is seen in context of the period. The Industrial Revolution saw a resurgence in Puritan ethics — urged on, whenever possible, by science, finding or leveraging particular strength in Social Darwinism. In The Debate Over Women’s Clothing: ‘Rational’ or Lady-like Dress, Justina Rodrigues explains how fashion fit in:
After 1850 the racial degeneration argument was strongly argued by social Darwinists. They contended that fragile and “wasp” waisted women would generate a debilitated race. Women, as a result, could no longer fulfill their natural, maternal roles because of the pernicious habit of compressing their stomachs. Their histrionics went as far as to suggest that England would be filled with a new inferior race. <41> It was a widely held belief that the coarse working poor were in danger of taking control from the weak middle-classes. <42> Darwinists also argued that “rational” dress made a civilized and intelligent society; they claimed that anthropological studies of primitive cultures proved that “backward” and “barbaric” people wore meaningless ornaments like bangles, bracelets, earrings, and the like. These dress reformers argued that ladies’ dress should evolve to the “superior ‘rational’ men’s standard.” <43> Mrs. E. M. King, secretary of the Rational Dress Society, was influenced by this trend. In her book entitled Rational Dress: Dress of Women and Savages she likened “savages” to fashionable women. <44>
Feminists were naturally drawn not only into science and social Dawinism, but regarding the matter of what Lelia A. Davis would, in her 1894 pamphlet, call “A Question Of The Day,” the question of women’s dress was motivated by three social changes:
- The entrance of women upon work hitherto considered outside their sphere.
- The higher education of women and the more common the dissemination of scientific knowledge.
- Organization among women.
Naturally, suffragettes and feminists would question the fashions of their time, but they didn’t all join groups such as the Rational Dress Society. Justina Rodrigues again explains:
The movement for women’s rights was loosely associated with the Rational Dress Society. Feminists agreed with doctors, social Darwinists and conservatives that lady-like dress was unhealthy and implicitly immoral, but differed in their views on restricting women within the boundaries of the home. Prominent feminists who were more concerned with women’s rights did not make dress reform their major cause. Indeed, Josephine Butler-by far the most well known Victorian figure of the women’s rights movement-was always immaculately lady-like in her dressing. <61> Mrs. Butler, being a product of the Victorian age, although a woman ahead of her times, could have been a believer of the mainstream Victorian notion of respectability in lady-like clothes. On the other hand, like Emily Davis, founder of Girton College, Mrs. Butler was concerned at being stereotyped as one of the “shrieking sisters” — loud manly looking female activists. <62> Some of the arguments that feminists made were that in order to achieve equality of the sexes, male sexual appetites should be controlled and lady’s fashion should be less distinct from man’s. Others stressed looking attractive as opposed to looking sexually attractive [an ambiguous directive, one might say]. <63>
The Rational Dress Society did not gain a large following and efforts by dress reformers saw pathetic results. ….Lady-like dress did not yield to critical ideology but rather prevailed in its own right.
Corsets were an early form of body modification, temporary cosmetic surgery, providing women breast augmentation and liposuction in the waist and stomach area. However, while it’s easy to blame corsets for holding stomachs in as well as holding women back, it’s clearly not that simple.
 The prevailing science that feminists wished to lean on was bad — and likely motivated by fear-based beliefs directly opposed to feminist ideology. The early feminists were living in a misogynist society, they were held by patriarchal stays which used the corset to control and interpret female dangers — including the dangers of women encroaching into male spheres via male modes of dress. Who wouldn’t want to cast off the corset, at the same time shirking the psychological shackles that the very debates conformed to? And what male wouldn’t prefer she literally stay in her place?
The prevailing science that feminists wished to lean on was bad — and likely motivated by fear-based beliefs directly opposed to feminist ideology. The early feminists were living in a misogynist society, they were held by patriarchal stays which used the corset to control and interpret female dangers — including the dangers of women encroaching into male spheres via male modes of dress. Who wouldn’t want to cast off the corset, at the same time shirking the psychological shackles that the very debates conformed to? And what male wouldn’t prefer she literally stay in her place?
Ultimately, however, the female identification with (and desire to conform to) beauty standards was clearly stronger than any of it. And while the fact that corset boning lead to marital boning is largely a biological imperative, that sound science is, by-and-large, currently not accepted by today’s feminists.
Corsets Are Too Sexy?
While I do not suggest that women should whittle away our waists as we while away our days in the constriction of too-tightly-laced corsets, I do believe there is good reason to at least examine the claims and assertions made about corsets by the 19th century medical community and the suffrage movement.
But if the medial claims weren’t true, if they were as exaggerated as the corseted female form, why?
 While many state that Victorian fashions for women were used as a means of control (and admiration through objectification) of women in a male dominated society, there is evidence to the contrary. In fact, many in 19th century, responding to fears of poverty and moral decay brought about by the Industrial Revolution’s over-crowding of cities, cried in outrage over the corset — but they saw the corset as impure and promoting impure behaviors among women (ever responsible for all of societies ills).
While many state that Victorian fashions for women were used as a means of control (and admiration through objectification) of women in a male dominated society, there is evidence to the contrary. In fact, many in 19th century, responding to fears of poverty and moral decay brought about by the Industrial Revolution’s over-crowding of cities, cried in outrage over the corset — but they saw the corset as impure and promoting impure behaviors among women (ever responsible for all of societies ills).
Victorian phrenologist Orson S. Fowler, an American, warned that wearing a corset excited dangerous “amative desires” by pressing blood to bowels. In Intemperance and Tightlacing, he argues that this made blood become “impure and corrupt,” caused “disease to the brain,” and inevitably led to “impure feelings” as “weak-minded” ladies were, obviously, easily prey to temptation. Illustrations mocking the too-trusting, if not cuckolded, husband conveyed such possibilities.
Perceived as (and raised to be) innocent, Victorian women on pedestals were void of any “animal feelings” such as sexual love, but this “special nature” made her a trusting, giving and warm person which, combined with her lack of intellect, made her not only prey to sexual seduction, but once introduced to such ‘sins’ she would be insatiable.
Such views of women convinced Victorian professionals that corset wearing led to such sins as hyper-sexuality and masturbation. In A Textbook on Sex Education (London, 1918), Walter Gallichen wrote:
The early wearing of stays is said to cause precocious sexuality. When it is known that a degenerate cult of tight corset wearers exists in England with a journal devoted to their craze between tightlacing and sex hyperaesthesia [heightened feeling] seems to be well established.
Ahh, so now the corset wasn’t just about seducing men, but ourselves. We were deemed dangerous dames because, poor things that we are, we’re too weak to resist sexual desires. We’d easily fall for any man, any time, any where. Worse yet, what if we opted to masturbate?! Men, as always, feared our ability to make choices. (In truth, what need do multiple-orgasmic creatures have for inconsiderate three-huffs-and-puffs-to-climax lovers who seek to control us?)
So, just how would you stop a corset-wearing woman from screwing around and diddling herself? Well, you get her out of that corset by any means possible — including scaring the crap out of her with exaggerated (or completely falsified) science.
According to this article on the brothers Lucien C. and I. DeVer Warner, founders of Warner Brothers (now Warnaco) knew the power of medical alignment selling foundation garments:
It took a couple of doctors to sell women on the idea that “rearranging” the human body via the old-fashioned corset was not practical. Doctors Lucien C. and I. DeVer Warner put their heads together and came up with a corset to fit a woman’s body, unlike other Victorian undergarments which “tied” her in.
They weren’t the first to sell corsets with doctor names, but they were among the first in the U.S. to push the “new” corsets; I’m sure it was made all that much easier (and profitable) with medical science telling those frightening anecdotal stories of death by too-restrictive corset.
Just where did the feminists fit into all of this? Well, that’s for part three.
What If Everything You Knew About The Corset Was Wrong?
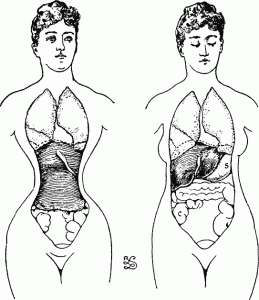 It’s fashionable these days for folks to denounce the historical use of corsets as akin to Chinese footbinding — an early form of plastic surgery.
It’s fashionable these days for folks to denounce the historical use of corsets as akin to Chinese footbinding — an early form of plastic surgery.
Corsets and tight lacing are said to have controlled women to their physical detriment; corsets have been blamed for breathing problems, broken ribs, curvature of the spine, hunchbacks, prolapsed uterus, miscarriages, hysteria and other mental illness, fainting spells, epilepsy, and even fatalities. Supposedly, in 1859, a 23 year old Parisian woman at a ball was “proved to be the envy of all with her thirteen inch waist; two days later she was found dead.”
As one who has held antique corsets in her hands, I find some of this a bit hard to swallow. Holding antique corsets which have been worn, one sees the evidence that the human body is not so easily molded; along with stretched fabric and folds from human flesh, there are torn seams and broken boning, all proof that female forms made the corsets conform to them.
 But you don’t have to take my anecdotal word for it; there’s an ephemera trail of advertisements to prove this too. This 1874 ad for Thomson’s undergarments features The Unbreakable, which by its claim that it “greatly reduces the risk of fracture, while permitting the use of most highly-tempered steel,” proves that women’s bodies forced damages on corsets and their structures.
But you don’t have to take my anecdotal word for it; there’s an ephemera trail of advertisements to prove this too. This 1874 ad for Thomson’s undergarments features The Unbreakable, which by its claim that it “greatly reduces the risk of fracture, while permitting the use of most highly-tempered steel,” proves that women’s bodies forced damages on corsets and their structures.
But you don’t have to take this to heart either — you can, at least for now, remain as firmly fixed on the idea that corsets were bad as you believe the horrible contraptions were on the female forms they mangled. You wouldn’t be the first…
In 1653, Dr. John Bulwer wrote in Anthropometamorphosis, Man Transform’d (aka The Artificial Changeling, London 1650), that ‘straight lacing’ was said to be the cause of “stinking breath” leading to “consumptions and a withering rottennesse.” (Bulwer also was anti-circumcision, but that’s another ‘piece’ altogether.) However Bulwer’s B.S. (consumption, for example, was tuberculosis and not caused by corsets; halitosis is rarely, if ever, a result of stomach issues, rottennesse or otherwise), is generally aimed to ridicule and condemn female vanity and following of fashion than it is aimed at helping physical ailments.
Fashion, especially women’s dress, has always reflected the the morals, values, and dynamic changes of society. And fashion (as well as its icons) have also been used to sway public opinion and create changes in society to reflect new norms. Which part of this rule, reflection of or tool used, is the corset?
Am I to believe that by the late 19th century the medical community — which was still neither treating female patients nor studying their physiology — suddenly cared about women? Even if they seemed to agree with the feminists of the time, the suffragettes, they seem too much like the proverbial odd bedfellows to me…
Let’s start by looking at the facts about where the so-called medical evidence of health problems from wearing corsets (such as in The New York Medical Journal, November 5, 1887) came from.
Fact: It was (and still is) easier to obtain permission to study the bodies of the lower and working classes. As with any ‘scandal’, the wealthy have the privilege of privacy — both in their lifetimes and afterwards. Not only are the wealthy protected from any examinations, but from stories about their lives and deaths — real or fanciful. Publicity could and would bring lawsuits. The poor or not-wealthy have less might to preserve any rights; prostitutes and others who either dropped dead on the streets or otherwise would have had their bodies dumped in pauper’s graves (and mass burials) have virtually no rights at death. These are the bodies science used. As a result, the information available would be skewed at best, completely false at worst..
Fact: The health of the lower classes was (and comparatively still is) horrible. Among the anecdotal examples of the corset as undergarment of death and destruction:
- A 21 year old prostitute who died of syphilis, consumption, and corsets while sitting in a police station.
- A chambermaid who was found dead after suffering from extreme stomach pains. Upon her death, her stomach was found to be nearly severed in half “leaving a canal only as narrow as a raven’s feather.”
These stories are horrific, yes; but are they accurate?
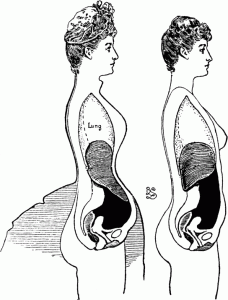 Clearly dead women had health problems, but from corsets alone? When you read such things (which are said to be documented in Fashion and Fetishism by David Kunzle), you simply have to consider the alternatives to “the corset did it.” These deaths are more likely attributed to general health problems of the poor and working class. Diseases such as TB, syphilis (and other STDs), reproductive problems from multiple pregnancies, dietary deficiencies such as rickets, etc. were incredibly common.
Clearly dead women had health problems, but from corsets alone? When you read such things (which are said to be documented in Fashion and Fetishism by David Kunzle), you simply have to consider the alternatives to “the corset did it.” These deaths are more likely attributed to general health problems of the poor and working class. Diseases such as TB, syphilis (and other STDs), reproductive problems from multiple pregnancies, dietary deficiencies such as rickets, etc. were incredibly common.
It’s more than possible that these stories have been exaggerated or even made up (Who would question the ‘findings’ or rush to the defense of a prostitute or a chambermaid?) to further an agenda. But if the stories were made up, why? What was the motivation, the agenda?
Come back Monday, for more…
After Stocking Panic, Women Made-Up
 I’ve researched and written a lot about vintage nylon stockings over the years because the history of nylon stockings is quite fascinating to me. I’m sure most of you have heard about the scarcity of nylon during WWII — just months after the new invention hit store shelves on May 15, 1940. Even silk stockings, second choice to the preferred fit and feel of nylon, were in very short supply as silk was also used for the war effort and the war itself interfered with over-seas shipments.
I’ve researched and written a lot about vintage nylon stockings over the years because the history of nylon stockings is quite fascinating to me. I’m sure most of you have heard about the scarcity of nylon during WWII — just months after the new invention hit store shelves on May 15, 1940. Even silk stockings, second choice to the preferred fit and feel of nylon, were in very short supply as silk was also used for the war effort and the war itself interfered with over-seas shipments.
The inability to get stockings fueled “Nylon Mania” and caused “Stocking Panic.” These terms are not flowery exaggerations. When shipments of stockings were announced, long lines and even mobs formed. It was so common place, jokes and cartoon strips about Nylon Mania abounded.
Women (and stocking-loving males) everywhere in the country were saying they’d kill for a pair of stockings; whether or not any of them actually did isn’t out of the realm of possibility… People weren’t always content to wait for stockings to arrive in stores, then form and wait in long lines to buy them. They formed mobs, sometimes attacking other shoppers; stockings (which retailed for about a dollar) sold for as much as $20 (that’s a month’s worth of payday loans back then) on the black market, which only incentivised robberies and other crimes. So commonplace was this mania, so connected to criminal activity, that in Chicago, police investigating a murder case used “Nylon Mania” to rule out robbery as motive simply because six pairs of nylon stockings ($120 worth of valuable property) had been left at the scene of the crime.
This is why you often hear jokes about guys getting “in” with a girl by bringing her stockings; like chocolates & cigarettes, stockings were such a luxury that they might buy you things that money might not!
Some of you may have been told by a relative, or otherwise heard about, how women during World War II had no stockings and so they ‘penciled in’ seams, using eyeliner or eyebrow pencil to draw lines up the backs of their legs to create the look of stockings. Here, 1942 Hollywood starlet Kay Bensel applied her faux stocking seams with a device “made from a screw driver handle, bicycle leg-clip, and an ordinary eyebrow pencil.”
But apparently this was not the only cosmetic approach to hiding one’s bare legs with Victory Hose. In a copy of The Professional Beautician (June, 1942), I found an ad which surprised me (I may surprise many of you with my finds, but many things continue to surprise me too!); an ad for beauty shop owners to stock Curley Colortone Cosmetic Stockings:
The vintage wholesale advertisement for professionals promises that each unit of Curley Colortone Cosmetic Stockings includes a jar of Colortone (in all popular shades) and a jar of Curley Foundation Creme (to give complete perfection) and clearly shows that salon product was also available. While not the graphic feast for public promotion this 1943 ad for Gaby Nu-Natural leg make-up is, I do have the Curley Colortone ad to thank for informing me about such vintage beauty products.
But don’t get too excited thinking these products were simply a matter of the war (or get overly upset thinking that companies dared to capitalize off of the war) because the January 1938 issue of Popular Science boasted “Cream Replaces Silk Stockings,” a new cosmetic “boon to the outdoor girl,” (who I suppose didn’t want to damage silk stockings with snags on twigs and other outdoorsy things). And in fact, the Smithsonian, showing us Leg Silque Liquid Stockings by the Langlors Company, says that such leg makeup had been available since the 1920s — but “it wasn’t until rationing was introduced during the World War II that the product became an essential commodity for many American women.” Heck, by then even Hollywood was impacted; unable to get stockings for the gams of their actresses and starlets, Hollywood created its own makeup stocking substitute.
This all brings us to another WWII joke:
Q: What’s a wife more afraid of finding on her man than lipstick on his collar?
A: Leg paint on his back.
PS American women weren’t the only ones suffering either; Miner’s had great success with its Seam Stick and Miner’s Liquid Stockings.
Excuse Me, May I Show A Movie On Your Antique Purse?
 On Saturday I got my first real antique purses — and, as usual, I’m obsessing over researching what I can about them. Today I’m going to inform you about the fascinating things I learned about antique metal mesh bags by Mandalian Manufacturing Company.
On Saturday I got my first real antique purses — and, as usual, I’m obsessing over researching what I can about them. Today I’m going to inform you about the fascinating things I learned about antique metal mesh bags by Mandalian Manufacturing Company.
First a bit of history.
Armor mesh bags by Mandalian are as sought after as those by Whiting & Davis. Though, admittedly, metal mesh and chain had been used for quite some time, Whiting is often credited for having developed the technique for the first mesh bags in 1892. He then partnered with Davis in 1896 and when the mesh machine was invented in 1909, Whiting & Davis acquired the patent. This not only affected the cottage industry of women who hand soldered the up to 100,000 links per bag, but limited big business. However, companies keep trying because the metal mesh bags were only becoming more popular.
One of these was Sahatiel Gabrabed Mandalian, an Indian immigrant * who was focused on quality more than quantity. This is noted in A) the remaining purses themselves; B) the quantity of advertising (Whiting & Davis papered the world promoting their larger production runs, while Mandalians’ ads and inventory were much fewer in number)’ and C) the number of patents Mandalian held — with quite a few in metal mesh and enamel application, as well as jewelry and other accessories.
One of the ways Mandalian separated his mesh bags was with the invention of applying crushed fish scale to the mesh, creating a ‘pearlized mesh’ the company promoted early on, as this vintage tag shows, Color-Vision-Bag, Trade Mark, Process patent Pending
However, the name most of these vintage bags sold under was Lustro-Pearl, exhibited here by this Mandalian mesh purse with original box and tag.
But fashion accessories weren’t the only things Mandalian envisioned — for his Lustro-Pearl, or his mesh metal. In the May 19, 1931, issue of Exhibitors Forum (page 6), this news:
“Lustro-Pearl” New Metal Type Screen
A new type metal mesh projection screen, known as “Lustro-Pearl,” has been placed on the market by Mandalian Manufacturing Co., of North Attleboro, Mass.
The advanced features claimed for this new screen includes: A surface treated with the purest of known chemicals, entirely free from gloss, eliminating all distortion to ordinary types.
Highest reflection factor known to reputable light testing laboratories, effecting a considerable saving of electric current.
Constructed so as to distribute sound very clearly and uniformly throughout the entire theatre.
Can be washed with hot water and soft brush without injury to its surface.
Affords clear view of any picture from any angle of observation, eliminating eye strain or discomfort to patrons.
Surface may be sprayed periodically for many years, and for this purpose, the company plans to loan for a period of ten years a complete up-to-date spraying outfit with each screen purchased, and furnish chemical solutions from time to time for resurfacing this type of screen.
Its high reflective qualities bring out objects in a manner which might be termed the nearest approach to three dimensional pictures, the company claims.
RKO Proctor’s 58th Street, New York, is among the first houses to install this new type of screen.
(This patent, #1,890,819, was issued December 13, 1932.)
But eventually even the better made and more stylized mesh bags by Mandalian couldn’t compete with Whiting & Davis who, by 1944, added Mandalian Mfg. Co. to their list of competitors they’d bought out. Sahatiel G. Mandalian would pass away just five years later.
I could find no record of whether or not that included the film projection screens — or if that business had folded long before 1944. Any info is appreciated!
*
UPDTATE: Per comments, Sahatiel was not Indian but an Armenian immigrant born in Constantinople, Turkey.
Cheap Thrills Thursday: 1907 Englishwoman’s Snark On Fashionistas
The piece, a little beauty titled “Woman’s Dress and Women’s Homes,” in which an Englishwoman ever-so-politely snarks about the mode of American dress, was written by Anna A. Rogers (originally in the Atlantic and then published in the November 4, 1907 edition of The Fargo Forum and Daily Republican). In the article, Ms. Rogers quotes an unidentified Englishwoman who had apparently spoken to an unidentified “writer in one of our western cities especially given over to the national passion for dress.”
The authenticity, sincerity, and/or seriousness of this piece is up to you to decide; as is Ms. Roger’s intent. But comments like “a slovenly ‘slavey’ attends the door,” sure are telling enough on their own.
This little bit of joy was discovered via the many hours I spend nerdily reading antique newspapers on microfilm at the Fargo public library (because, as they say, “Library, library, more than a book!”), and so my cost was free — unless you count my taxes, which I am most happy to see go to the preservation and presentation of such things.
Whatjamacallit Wednesday: Sewing Hat For A Rainy Day
I’m a dork. I know it, and now you’ll know it too.
When I spotted the cover of this 1975 Simplicity sewing book — “updated!” — I had to have it.
I had to have it because I actually thought that they’d have instructions for how to make the hat. Yes, I thought that 1) the kitschy fisherman’s hat adorned with pincushion (with pins, no less), scissors, and measuring tape-turned-bow, would be awesome to wear going to rummage sales on those rainy days, and that B) a book of sewing instructions would actually include instructions for creating the item featured on the cover.
Now you might agree that I’m just plain silly for the first thing; but don’t you think a person ought to expect the latter? But no. Apparently Simplicity thinks making the hat is obvious enough. Which I suppose is better than being like that super-annoying and frustrating Science Channel show, How It’s Made, which informs you that markers are made by putting felt into a plastic tube and inserting ink into the absorbent felt. A Duh. That’s not how something is made, that’s how something is assembled from already made parts.
But my point is, while I can buy a bright yellow rain hat and all the sewing supplies, I have no idea how to attach said sewing supplies without ending up having to wear a pirate’s eye patch — and telling people that I was blinded by my own lack of sewing skill, causing a scissors to fall from my kitschy hat & skewer my eyeball.
None of this, however, dampens my desire for such a hat. Sew So, if you know how to make such a hat — that is safe enough to wear — please do tell.
I See London, I See France, I See Lessons In Barbie’s Underpants
 Because my first Barbie dolls had been my aunt’s, I had a lot of the original stuff, including those (now highly collectible) palest blue whispers of chiffon pleated underpants. I remembered being struck by the incongruity of such angles — the square-ish lines of the boxy panties themselves and the triangular points of the pleats — against the round curves of plump plastic. As I slipped them over Babs’ firm flesh, I wondered what her shape would do to the shape of those panties… Miraculously, some of the pleating remained when Barbie wore them — and in fact, the pleating was fully retained once removed from the doll. These were things I was highly suspicious of.
Because my first Barbie dolls had been my aunt’s, I had a lot of the original stuff, including those (now highly collectible) palest blue whispers of chiffon pleated underpants. I remembered being struck by the incongruity of such angles — the square-ish lines of the boxy panties themselves and the triangular points of the pleats — against the round curves of plump plastic. As I slipped them over Babs’ firm flesh, I wondered what her shape would do to the shape of those panties… Miraculously, some of the pleating remained when Barbie wore them — and in fact, the pleating was fully retained once removed from the doll. These were things I was highly suspicious of.
I wondered if those puffs of pleats remained beneath Barbie’s outerwear… They weren’t really visible; Barbie did not suffer from visible panty lines either. But like that refrigerator light problem, there was no way to see-to-believe, no way to really know.
While many blame Barbie for a plethora of society’s ills, I’m not so convinced. I learned many things from Barbie, including, but not limited to, the pure impossibility of comparing myself to a doll (let alone coming up short in such a comparison).
Barbie was a doll, her movements were not only dictated & restricted by manufactured bendable knees & stiff elbows, but whatever limited movements Babs had could only be made at my whim. Her permanently arched foot did not relax when her shoes were removed, nor when she went to sleep. (This, I would learn years later as a department store sales person, was quite probably the most realistic thing about Barbie.) When I cut her hair, it did not grow back. Ever. When her leg popped-off at the hip, you could just press it firmly back into place; no blood, no guts, just the glory of fixing a problem yourself.
Barbie was not real and I knew it.
Her lack of areolas and nipples did not make me question the existence of mine. The enormous size of her breasts and their skewed proportionality did not make me question the size and proportion of my mother’s bustline, that of any other female that I knew, or my own breasts when I developed them. Barbie’s flat tummy did not make me question my plump belly or that of any other female; hers was hard unforgiving plastic, ours were flesh — as flexible, purposeful and forgiving as our arms. Our bodies existed for more than posing, for draping fabrics, for pretending. We are not dolls; we are a human.
Of course, as a child, I didn’t exactly articulate these things to myself or anyone else; these were simply the lessons of play. (Are those the ingrained messages they want to protect children from?)
OK, so Barbie’s hyper-beauty was unrealistic, so what? I had a brain. I was no more in danger from this fashion doll than boys who played smash-up with Hot Wheels cars were from driving like the world was a demotion derby they could just get up and walk away from. Kids can tell reality from pretend, especially when they have emotionally & intelligently available adults who answer questions and talk with them, not at them.
(This is not to say that Barbie, media images, etc. do not have an impact; but that’s more a matter of a collective accumulation of messages. And I’ll continue to pull at those threads.)
However — getting back to Barbie’s pleated underwear, what started all this in my mind was spotting these vintage knife pleated panties.
In jadeite green and blushy-peach, they are color variations of Babs’ fancy sheer knickers!
I instantly thought of the mysteries of those angles on Barbie’s curves, of how I wondered just how real flesh would react with those pleats… Puckers & folds in your pants or beneath a slip-protected skirt, would they be there under your clothes? Or would your flesh fill them out, curves rubbing-out the angles? If they were there, what would they feel like? Would they remain when you took those panties off? Puckers & folds, those are usually considered imperfections — yet here they are, for living humans, not just dolls.
These vintage panties are beautiful little mysteries to me. And until I find a pair in my size, this is how they shall remain to me.
Big Bottom Girls Are About To Make The Fashion World Go ‘Round
In 3,500 stores, Walmart will be doubling the space given to Hanesbrands’ plus-sized apparel line Just My Size — an extended line of Just My Size women’s clothes, including dress pants, sweaters and other merchandise beyond the underwear and jeans.
Hanesbrands research found that 60 percent of women shopping at Walmart fit plus sizes, said John Marsh, senior vice president and general manager of the manufacturer’s casual-wear division. About 40 percent of overweight women are comfortable wearing clothes designed as plus size, rather than buying extra-large of regular garments, he said.
Average sized women (for that’s what size 12 and up is!) are comfortable with the “plus size” label because we know that honest-to-goodness clothing designed at a plus size is made to fit bigger bodies; you don’t just add an inch or more all over and think, “Well that’s that! Now it will fit.”
This reminds me of last week’s episode of Shark Tank…
 When fashion designer Gayla Bentley appeared, asking for a $250,000 investment (for a 20% stake) in her company so that she could make beautiful clothes easily accessible for large women by expanding her business to include a store to cater to them (and better brand herself), she was met with the a-duh moment from a supposedly savvy investor.
When fashion designer Gayla Bentley appeared, asking for a $250,000 investment (for a 20% stake) in her company so that she could make beautiful clothes easily accessible for large women by expanding her business to include a store to cater to them (and better brand herself), she was met with the a-duh moment from a supposedly savvy investor.
Kevin O’Leary, ever-arrogant (and admittedly the show’s love-to-hate guy), said, “Is it possible that larger sized women (and don’t beat me with at stick) don’t care about fashion as much?”
As if a 60% market share were just that easily ignored (that is has been is an enigma wrapped in a bitter wienie coating), Bentley (completely charming as well as intelligent and talented) continued to educate he and other doubters with the facts, including her own success; currently the designer sells her products wholesale and online and last year her sales were $500,000. (Yet no bank would give her a loan.) You can watch the episode here (and find out more at Wallet Pop, but the final outcome was that Barbara Corcoran and Daymond John (of FUBU fame) went in 50-50; now we just have to wait to see Bentley’s efforts to bring real plus size designer fashions to department stores near you & I.
While I’m in no way comparing Just My Size &/or Hanesbrands to Gayla Bentley’s fashions or those by any actual designer, I am encouraged that big business is beginning to see big T n A as a way to fatten their own bottom lines.
Strange Creatures Are Wiggling Their Way Down Your Legs – And You Like It
Knit your own Space Invaders leg warmers, yo.
Uh, My Eyes Are Up Here, Bud.
Every female who has had to remind a male to look her in the eye (or at least her face) as opposed to looking at her breasts when talking to her — and that’s a whole lot of us! — will find this item annoying.
In the October issue of Cosmo, Gossip Girl‘s Penn Badgley models this “winking” sweater by French Connection:
Do men really need to be encouraged to look at our boobs? Do they really need to be more confused about where to find out eyes?
The official name of the sweater is “Lush Lashes” — and while they may only charge you $128 to purchase it, the cost to women everywhere is much, much, higher.
Fabric Swatch Friday: Of Hippies & Stoned Flappers
Retro clothing that amazes me: two-piece bell-bottomed pantsuit with a wild print of a Flapper, flowers and rainbows.
It’s Not Blackface When They Have Black Faces, Right?
I love this vintage cotton novelty print blouse from the Bahamas — well, at least until I spotted the three Bahamian singers…
Then I worried that they looked a lot like minstrel performers in blackface. But black persons can be shown as black persons, right?
Uh, I don’t think I can send myself, a white woman, out into the world unless I’m absolutely certain that the rest of the world can tell that this is not racist.
PS I know this isn’t Black Americana, it’s Bahamian. But I’m using that tag so folks can find quasi-related stuff; such is the way of folksonomy.
There’s A Gnome Reading On Your Chest
The Whole Thing Is Making Me Mod As Hell
So cut-out the flower power & make your boots go-go away.
Desperately Seeking 80’s Madonna Fashions?
UPDATE 10/18/2014: I’ve a pair of the black Desperately Seeking Susan boots for sale in my Etsy shop!
Speaking of 1980’s-Desperately-Seeking-Susan Madonna & boots…
Fans of the film Desperately Seeking Susan will remember that the whole hullabaloo started when Susan (Madonna), trades in her fabulous jacket for a pair of boots spotted in the window at Love Saves The Day (the old, original location, not the new one in New Hope, PA) — and then Roberta (Rosanna Arquette) buys the jacket, gets hit on the head and, trying to discover who she is, uses the key in the jacket’s pocket to open the Pandora’s-box-of-a-port-authority locker, setting off a romantic comedy of mistaken identity. An entirely awesome film. Seriously. Just try not to enjoy Desperately Seeking Susan.
With the 80s fashion comeback, blah-blah-blah, how would you like to be so hip & retro it hurts and have these boots? (Frankly, back in the day, I wouldn’t have been caught dead in them — too copy-cat, even though I was dressed as scandalously; but now those boots are kitsch-a-licious — now with added irony!)
Bakers – Leeds owned the license to copy the boots designed by the film’s Costume Design Assistant, Alison Lances, but Town & Country knocked-off a netting with sequins over vinyl version. Frankly, it would be hard to tell the difference, right?
But good luck finding either of them — if & when you do, be prepared to pay several times the original $49. Yup, even for pleather.
However, crafty girls could likely figure out how to adopt this vintage hairpin lace crochet pattern to make the netted boot overlay and add sequins, right? (Click this larger image from MadonnaUnderground.nl to guide you.)
If rhinestones & shiny bling aren’t exactly your thing, you can opt for more punk studs — no, not men with attitude; boots with stud decorations, dears. Alyssa Zukas AKA Two Sting Jane does — and she even shares how! (If that link doesn’t always work — and it is wonky, giving 404s, try the DIY link and scroll; it’s worth it!)
And, because what are shoes without the right handbag, why not make a purse version of the iconic skull suitcase.
However, if you never ever would have traded costume designer Santo Loquasto’s jacket for those boots…
Well, copies of those jackets were licensed and made “retail available,” just like the boots, and advertised on MTV.
Made by Identity, Inc. &/or Creative Embroidery Corp. (I say “and/or” because both were marketed by Targeted Communications, Inc., so they could have been the same company.), the jackets have a hefty price — if & when you can find them.
If you can sew or at least embroider, you can add the pyramid & eye, like that on a dollar bill, and the phrase “Novus Ordo Seclorum” to a jacket — just like Awsumgal did — sure, it’s a doll’s jacket; but it’s the same steps, just a different scale.
So get crafty and create your own fashion homage to the 1980’s that you so desperately seek. Aidan Quinn sold separately.








































